One of the most significant advantages of running a business is you can have multiple product offerings. But many miss out on revenue and truly impact their bottom line – because they don’t cross-sell and upsell. And that’s unfortunate because those sales techniques can transform any business. So, what are cross-selling and upselling?
This article will provide everything you need to know. And as you read on, note that “product” refers to physical and digital goods, including services.
Cross-selling
Cross-selling is the process of encouraging someone to buy additional products that are either complementary or useful to the customer.
Good cross-sell offers typically provide unfulfilled value by the original purchase, but they don’t have to be related. You can cross-sell new products and related items as additional purchase options.
Here are some good examples of successful cross-selling:
- The car dealership convinces the couple to buy a brand-new SUV. Upon closing the deal, the sales rep offered them rustproofing (supplementary product) to protect the vehicle from rust. The couple took the offer, increasing the order value.
- An educator has a bookkeeping course that's doing well. However, they also have an accounting course that could be doing better. So the creator decides to cross-sell the accounting course to students who complete the bookkeeping training. The offer here is complementary to the purchased product.
- A coach that sells a barista course is cross-selling their ‘how to start a business' training to students who complete it. The course about starting a business isn’t particularly closely related to being a barista. But it makes sense since someone may want to start their coffee shop.
- How about something simpler? Think about when you last visited a fast food restaurant. They usually ask if you want to make your order a meal, and that’s a cross-sell. The fries and drink complement the sandwich. The customer is happy, and the company successfully impacts its order value and profit margins.
In each example, the offers are items of significant value or complementary products. The important thing to remember is that any valuable product can become a successful cross-sell.
Upselling
In contrast to cross-selling, upselling is about encouraging your customer to upgrade their product in some way – usually by buying something extra, higher priced, or a more expensive product.
It’s an additional product that would improve the purchaser’s experience. For example, convincing your customer to add enhancements, take the premium option, or buy a better version.
Here are some good examples of successful upselling.
- A Youtuber offers one mastermind group program subscription where people help each other improve their businesses. One day they decided to offer each mastermind group member a growth session package of five one-on-one coaching times to increase sales. The offer upgrades the product for current customers.
- An educator teaches people how to start an online business, but they also have other essential services. So as an upsell, they offer a done-for-you service to help students set up their websites. The done-for-you website setup offer is a related or complementary product.
- Revisiting the fast food restaurant example earlier, an upsell would be adding tomatoes, cheese, and pickles to your sandwich. Those things transform the sandwich into a better product for you.
The critical thing to remember is that the offer needs to upgrade the customer experience. It can be a higher price item, but not always. It can also be much less than the one in consideration or the purchased product.
What data says about cross-selling and upselling
Sales techniques like cross-selling and upselling help creators achieve sustainable growth. They ensure sales continue by allowing businesses to generate extra revenue without having to seek out new customers all the time.
Here are some insights to consider.
- The probability of selling to current customers is significantly greater than to new customers. According to the book, Marketing Metrics, your chances increase by 60 to 70 percent.
- One analysis by Forrester found upselling and cross-selling strategies were solely responsible for an average of 10 to 30 percent of eCommerce revenues.
- Another study by HubSpot revealed almost half of businesses get 11 to 30 percent of their revenue from upselling and cross-selling.
- Creators that leverage SMS may see greater success with these sales techniques. Research suggests 75% of customers aged 44 and below prefer text message communications. And the CTR (click-through rate) for offers sent by text messages is 9.18% higher than other digital channels.
What’s better? Cross-selling vs. upselling
Research suggests upselling drives more sales. The sales tactic drives over 4% of online sales, while cross-selling brings in about 0.2 percent.
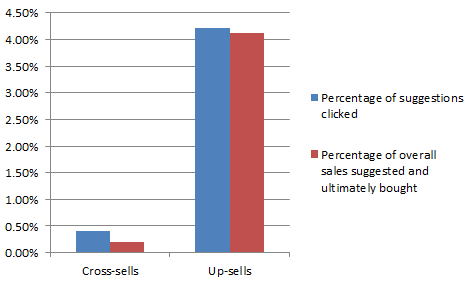
Both sales techniques also positively impact conversion rates.
For example, a new prospect can decide to buy because they could get specific upgrades from the same website. Similarly, someone who sees you have all other related items may choose to get everything else from your business for the convenience.
However, looking at the conversion rate alone, upselling is much better. That’s because the likelihood of a ‘yes’ is higher since the customer has already bought something.
The upselling and cross-selling sales techniques can bring extra revenue from your existing customers and new ones. That can potentially transform your business, so use both sales tactics strategically.
Your offers should meet the sweet spot between value and cost. In other words, your upsells and cross-sells should make sense price-wise and value-wise.
How to cross-sell and upsell in your business
By now, you know the benefits of cross-selling and upselling.
These sales techniques (or marketing tactics) help creators sell more products with less effort and resources. They require fewer marketing dollars and time, which leads to increased revenue and profit margins.
Implemented strategically, you can provide more value to customers while increasing income, and without the typical recurring expenses.
Cross-selling and upselling will increase your average order value and customer lifetime value and improve brand loyalty. Here’s how:
- The average order value should go up because people usually make more purchases when given sensible opportunities.
- Your customer lifetime value should increase because you’re keeping people happy by helping them get what they want through cross-selling and upselling. Also, both sales techniques help ensure your audience isn't underserved, improving customer experience and customer satisfaction. Those things directly affect customer lifetime value because happy customers stick around.
- Customers who get what they want tend to renew their subscriptions or return for other purchases. This usually affects brand loyalty positively. In addition, brand loyalty impacts the referral rate since happy customers often refer new prospects.
Here's how to implement cross-selling and upselling in your business, including tips and best practices.
1. Understand your customer
You may already have a basic understanding of your customer. But do you truly know what they want and the most effective ways of selling to that audience? Do you know the intent of new prospects when they arrive at your website?
You must go beyond a basic understanding of your target audience for effective cross-selling and upselling. And one way of doing that is to create buyer personas, which are fictional representations of your target customers.
Going through the process of creating buyer personas can help you understand the audience better and predict what they would do after purchase. You may also gain a better grasp of their goals and challenges.
These things are critical for identifying the most helpful, relevant suggestions or additional products to cross-sell and upsell.
2. Use suggestive selling
One of the most important aspects of cross-selling and upselling is knowing how to push without annoying the customer. And that’s where suggestive selling comes into play.
Suggestive selling is a sales approach where customers receive guidance for upgrades or additional products. It’s essentially the intentional practice of cross-selling and upselling. But it isn’t pushy.
Rather, the goal is to plant the seed, so to speak, making it more likely that customers will get the additional product or enhancement. A good example is, “You’ve got free shipping, but so you know, there’s one-day shipping if you want this to arrive much sooner.”
That statement makes the customer aware of other shipping options. As a result, they may change their minds and opt for faster shipping instead of free shipping.
How about another example? A statement like, “you might want to take the corporation tax course too if you’re opening your own business” – plants an idea. The course creator could make the offer at the pre-purchase stage or after their original purchase.
3. Build out new customer journeys
The customer journey is a visual storyline encompassing every interaction or engagement consumers have with your business or product. It helps identify how people may use your offers and at what point to cross-sell or upsell.
Your new customer journey map can be simple or complex, depending on your business model and product. For example, a bookstore might have purchase, service, and customer loyalty as the main stages, with many potential consumer actions within each.
What is likely to happen after the customer buys a specific product? How can you use that information to build trust? What is the customer most likely to purchase next if you offer it?
You can get answers to questions like those from your new customer journey map. It will also help you design a strong sales funnel.
Sales funnels explained
The sales funnel is a hypothetical path prospect take to become paying customers. It's closely related to the customer journey, except more focused on the sale than every single consumer interaction or engagement.
Think of the sales funnel as a tool for tracking and moving prospects and leads through the buyer journey. Monitoring and examining your sales help optimize marketing efforts and conversion rates.
A typical sales funnel can have the following (from top to bottom).
- Prospects
- Lead qualification
- Intent
- Sale/Lost
As you can see, the funnel begins at the top when prospects initially discover your product. Then those prospects become leads after taking a genuine interest in your offer – not before.
For example, someone who downloads your free eBook and ends up in your email list isn't yet a lead. They have to take another action that signals interest in becoming one.
Once interested, the consumer begins to show intent, such as booking a call or adding products to their shopping cart page. Finally, the interaction is marked as a successful sale or loss, depending on how the customer proceeds.
Like the buyer’s journey, your sales funnel will help you target potential customers with the right type of content to move them along. You can deliver such content through email, blog posts, social media posts, etc. However, you cannot design a strong funnel without knowing your buyer’s journey.
4. Mind your timing
It’s essential to be strategic with the timing of your offers. You must present each one at the right time.
For upselling, the goal is to convince the customer to upgrade to a product that gives them more value. As such, the offer must make sense, and the same goes when cross-selling. In general, your best chance to upsell is during the purchase. And the offer should be a relevant upgrade to the original purchase.
As for cross-selling, the goal is to persuade someone to buy another service or product. And there's no particular right time to do it. You have to see the opportunity to cross-sell when it arises.
For example, if someone bought a course on bookkeeping, they may be interested in your accounting course. The offer doesn’t have to complement their original product, but most successful cross-sells do in some way.
Best practices for upselling:
- Provide relevant product suggestions as the customer is making the purchase.
- Present your offer when the customer needs additional features.
- Introduce your offer when the consumer reaches a success milestone with a logical opportunity for expansion.
Best practices for cross-selling:
- Suggest additional products as the customer is about to buy.
- Make relevant suggestions that are no-brainers for customers.
- Pick things appropriately priced so the consumer needs less mental energy to accept. It can be a lower price or lower price item. The cost just has to make sense to the consumer.
- Don’t overload the customer by making too many product suggestions.
Further, best practices for cross-selling and upselling overlap. That means you can apply them to both sales techniques depending on your overall goals and business model.
5. Make good use of your key pages
You can leverage your most important web pages (e.g., product page, checkout page, etc.) for upselling and cross-selling. For example, you can include “people also bought” additional item suggestions on every product page. Similarly, you could feature related products or similar products on the checkout page.
So your key pages can do the selling for you.
Let's look at some brand examples, starting with the following upsell by Udemy.
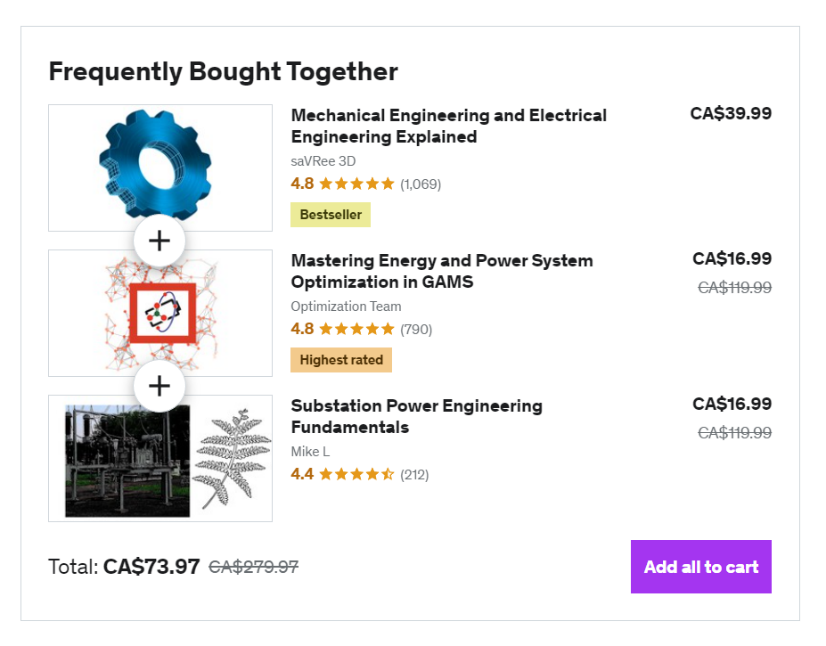
As you can see, the company is leveraging its product page to upsell the customer. They suggest the customer pick up additional products or courses to enhance their knowledge immensely.
The relevance of the product suggestions makes it more likely that the consumer will grab the offer. With upselling, related products work better compared to random product recommendations.
Here’s a cross-sell example from Microsoft.
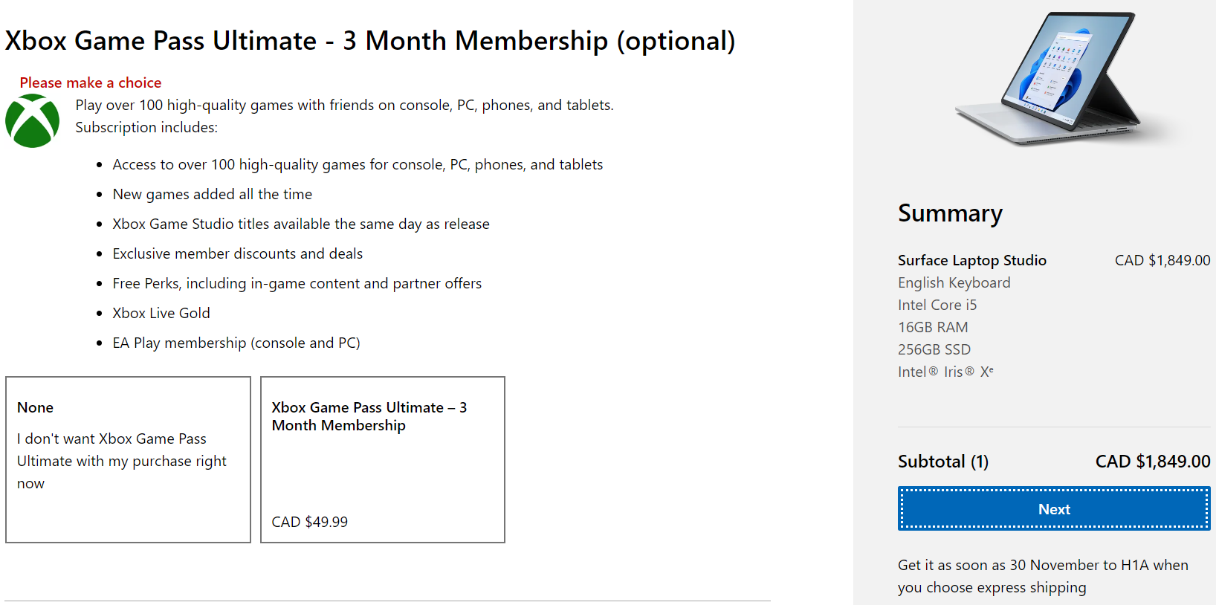
The Xbox game pass cross-sells works. That's because people who buy powerful computers tend to enjoy video games. It’s a somewhat related product, though that’s not necessary with cross-selling. The offer has to make sense as noted earlier.
6. Sharpen your in-person sales techniques or skills
One of the best ways to improve your in-person conversion rate is to practice active listening.
This is a communication skill where you do not just hear words but also deeply understand the person’s intent. It requires you to become an active participant in the communication. So you can easily identify when customers are ready for another offer.
The key elements of active listening are as follows (in the context of sales).
- Pay close attention – Give the customer your undivided attention.
- Show the customer you’re listening – Acknowledge the message or conversation. Use body language (e.g., nod your head, smile, adopt an inviting posture, etc.) and quick acknowledgment responses (e.g., yes, aha, etc.).
- Ask questions – Clarify statements and dive deeper into what the customer is thinking by asking questions. Oftentimes, people withhold information that they think isn't important to conversations. Questions can help them open up and give you the information necessary to segway into a cross-sell or upsell offer.
- Don't interrupt unless necessary – Most people find interruptions while conveying a message annoying. As such, you should be mindful not to interrupt the customer while speaking. Plus, letting them talk almost always provides additional details you can use to close the sale.
- Respond aptly – Show the customer respect and understanding. Be truthful and straightforward with your responses.
7. Champion the right skills for your sales team
If you have a sales team, your sales reps must master the fundamentals of cross-selling and upselling. And even if you don’t have a sales team, as noted earlier, sharpening the right skills will greatly affect your success.
Such skills include deep discovery, articulating differentiators in meaningful ways, and having a framework for demonstrating value. These practices should be part of your daily operating rhythm.
- Deep discovery: This is using effective questioning to uncover customer needs or pain points and cross-selling or upselling the appropriate product. People who practice deep discovery are great active listeners.
- Articulating differentiators: It’s easy to rattle off product features. The real challenge is conveying those features in a way that means something to the potential buyer. Make them care about the benefits of your upsell or cross-sell offer.
- A framework for value: There’s no better tool than a framework for effectively demonstrating value to customers – especially if you manage a sales team. The value framework is the principles that can help you win sales, usually in the form of a document. Your framework should clearly define the key value drivers that can push the audience to action.
8. Develop a good closing mindset
A good closing mindset means doing things that facilitate sales from the start. It’s focusing on loving and caring for your customers, putting their interests first. And factoring customer needs into your decision-making process.
For instance, recommending a higher-end item or better product because that is what’s best for the customer – not for revenue's sake.
Think of each sale as a continuation. You are building relationships with people to keep serving them on their journey. A good closing mindset makes customers more likely to say 'yes' to an upsell or cross-sell offer.
9. Use the right platform or online store solution
Adding upsells and cross-sells can be challenging when you have to add them to your website (or point-of-sale system). After all, it’s a process that often requires technical or programming knowledge. But cross-selling and upselling can be much easier with the right solution.
Your online store or subscription platform should facilitate these sales tactics. At a minimum, good solutions will let you do the following easily.
- Cross-sell and upsell additional items, such as related or frequently bought together products.
- Recommend additional products in the customer’s shopping cart.
- Recommend products after the customer checks out.
For example, Subkit enables the subscription model and lets online creators easily upsell and cross-sells their products. You can even collaborate with other businesses to cross-promote each other or bundle subscription offerings and share revenue. Such capabilities also increase your average order value. Get early access.
10. Suggest upsells and cross-sells in your emails
Email is an excellent channel for upselling and cross-selling. It’s the perfect opportunity to elicit interest in other products, and many successful brands use it.
For instance, you could send complementary items or upgrade suggestions after someone buys your product. This can be attached to the “thank you” or “receipt” email.
11. Bundle products for cross-selling and upsell
Another great way of using these sales tactics is to offer product bundles. This is grouping various products to sell them, typically at a lower price than if sold separately.
Some people call that a bundle-sell, and it’s one of the easiest ways to upsell and cross-sell. You saw the marketing technique in action with the Udemy example shared earlier.
When bundling products for upsell and cross-sell, the best way is to do either of the following.
- Suggest the bundle option alongside the desired main product to existing customers and new prospects. That way, people can decide to grab the bundle instead.
- Suggest a bundle after the purchase, such as upgrades, complementary products, similar items, or your best sellers.
Subkit makes it easy to do any of the above.
For example, Subkit creators can bundle and sell physical and online products (including sessions). You can even package subscription offerings with products from other businesses and share revenue (collabs). Get early access.
Stop leaving money on the table
Cross-selling is about suggesting any product with the initial purchase (complementary items, similar items, or completely different products). Upselling is upgrading or enhancing a solution through complementary products. And they are both powerful tools for realizing higher revenues.
When coaches, educators, and YouTubers don't cross-sell or upsell, they leave money on the table. That’s because a customer's revenue potential doesn't typically end after one sale. Instead, their buyer's journey continues, and you can lose them to competing brands.
Why put all your energy into selling a single product and miss out on potential long-term profits?
Upselling and cross-selling also encourage customer loyalty. The more additional items people buy from you, the more likely they'll remain your customers long-term.
Further, these sales techniques positively impact customer average order value and lifetime value. But you'll need a keen awareness of your audience's needs, optimal timing, and empathy for effective cross-selling and upselling.
That means knowing where people are in the customer journey, their potential feelings, what they need most, and which products will be of interest.
Use suggestive selling to make the ‘yes’ easier for customers. If suggesting products through a pre-recorded video, focus on sharing the value of the optional offer.
Lastly, ensure every cross-sell and upsell product suggestion is a potential natural next step for the customer (the right product). This is essential, and while commonplace, every brand has slightly different approaches when using these sales tactics. Never promote anything surprising or entirely out of the left field for the best results.
Turn your service, product, or expertise into recurring revenue. Cross-sell and upsell to your customers with ease, and much more. Get early access to Subkit.
